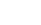Hunan Province is located in south-central China to the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and south of Dongting Lake.
Area: 211,800 km2
Population (2023): 65.68 Million
Capital: Changsha
Divisions: 13 cities, 1 autonomous prefecture, 122 counties and county-level cities.
Geographic location
Hunan Province lies in south-central China between 24°38'-30° 08' N and 108°47'-114°15' E. It is named after its location which is to the south of Dongting Lake (Hu is ‘lake’ and Nan is ‘south’ in Chinese). It covers 211,800 square kilometers (81,776 square miles) which is 2.2% of China. It is bounded by Jiangxi Province on the east, Chongqing Municipality and Guizhou Province on the west, Guangdong Province and Guangxi Autonomous Region to the south, and Hubei Province to the north.
Geology

Photo source: hunan.gov.cn
Hunan is mountainous and hilly in the east, west, and south. It is hilly with basins in the center and plains in the north. Its central and northern parts form a low and U-shaped basin facing north, with Dongting Lake as its center.
Huping Mountain in Shimen County, Changde, is its highest mountain, with an elevation of 2,009 meters. Its lowest point is in Huanggai Town, Yueyang at only 21 meters above sea level.
Dongting Lake is its largest lake and is China’s second largest freshwater lake. The Xiangjiang, Zijiang, Yuanjiang, and Lishui Rivers are Yangtze’s four main tributaries. It flows through Hunan, into Dongting Lake at Chenglingji, Yueyang.
Climate
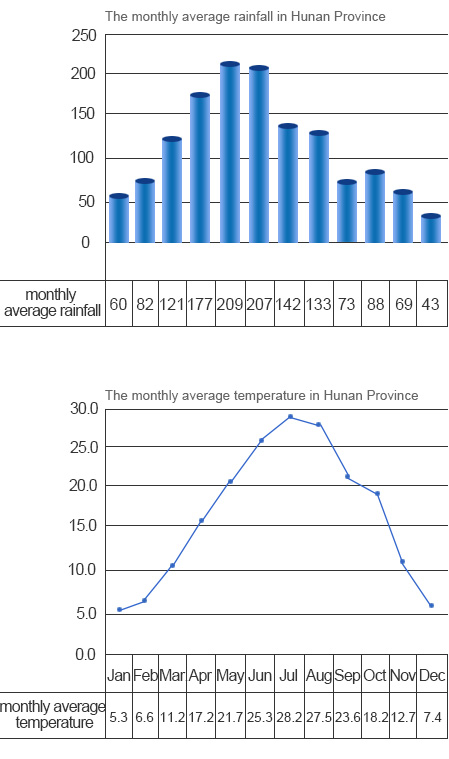
Hunan has a continental, subtropical, seasonally-humid climate with four distinct seasons. It has abundant sun, long frost-free periods, and abundant rainfall. The annual sunshine duration is 1300-1800 hours. The annual average temperature is 16℃-18℃. It is frost-free 260-310 days a year. Annual rainfall is 1200-1700 mm which is favorable for agriculture.